MongoDB Atlas is a fully-managed cloud database developed by the same people that build MongoDB. Atlas handles all the complexity of deploying, managing, and healing your deployments on the cloud service provider of your choice (AWS, Azure, and GCP).
An application deployed within Cloud Foundry can leverage MongoDB Atlas in a variety of ways:
- App configuration: Manually create a cluster, then get the connection string which you will use in your application.
- User-provided Service: This option extends the previous one and basically means that the connection string can be used to create what is called in Cloud foundry language a User-provided service which is simply a means to enable developers to use services that are not available in the marketplace.
However, these options have some drawbacks:
- Manual provisioning
- Poor self-service experience we are looking for
- Can’t set quotas to control services usages
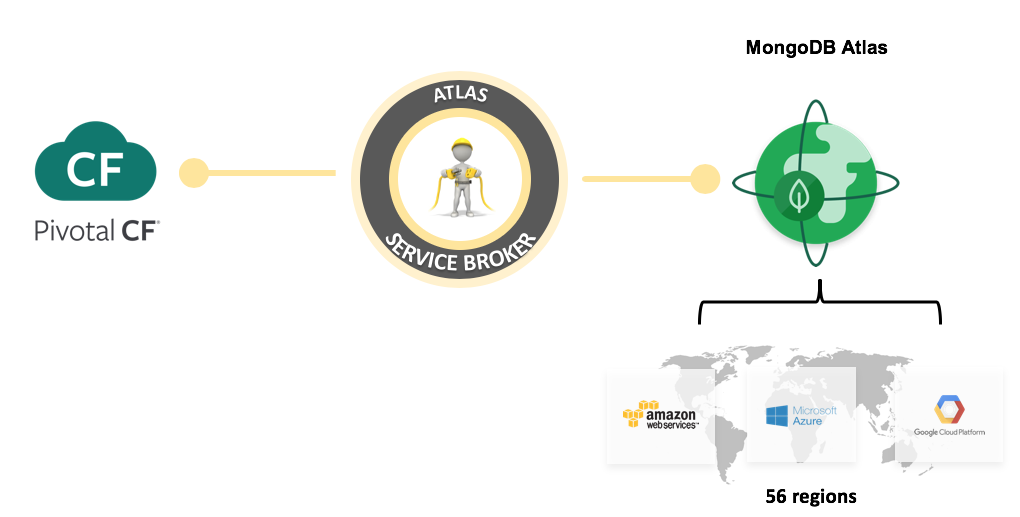
There is a third way, the ultimate holy grail in providing an amazing self-service experience is to use the Open Service Broker API project. This project is an open source effort sponsored by Google, IBM, Pivotal, Red Hat, SAP, and many others. The intent is to provide a simple set of API endpoints which can be used to provision, gain access to and managing service offerings. In our scenario, we will create a service broker that will be used by Cloud Foundry to provision MongoDB deployments in MongoDB Atlas.
Cloud Foundry exposes its services in the Marketplace for users to consume. The service manages the provisioning and de-provisioning of MongoDB deployments and provides the necessary credentials for applications.
Don’t We Already Have a PCF Tile for MongoDB?
For those that wish to deploy and manage their own MongoDB deployment within a PCF infrastructure, there is a PCF tile for MongoDB. While using this tile does allow you to deploy MongoDB within your infrastructure it does require setting up MongoDB Ops Manager in your environment as well as making sure you have enough resources to accommodate the MongoDB deployments.
By leveraging the Service Broker and MongoDB Atlas you Reduce management complexity/overhead as well as provide:
- A true Marketplace experience
- Support for many compliances (i.e: HIPAA, PCI, etc.)
- Access more comprehensible deployment sizes (T-shirts)
- Multi-Cloud deployment strategy
- The flexibility to deploy into MongoDB Atlas’s 56 regions utilizing any of the 3 majors Cloud Providers (AWS, GCP, Azure)
- End-users can take immediate advantage of any new capabilities of MongoDB Atlas.
Getting Started With the Service Broker for MongoDB Atlas
To get started, create a MongoDB Atlas account and create an Organization. You’ll also need to configure access to MongoDB Atlas API by creating an API Key. Please refer the to links given for full details.
To get the newly created Organization’s ID. This is simply done by clicking on the “Settings” menu on the left.
The next step is to authorize PCF to communicate with your MongoDB Atlas account. If you have properly followed Cloud Foundry deployment recommendations, this part gets really easy. Below is a simplistic view of the recommended deployment topology.
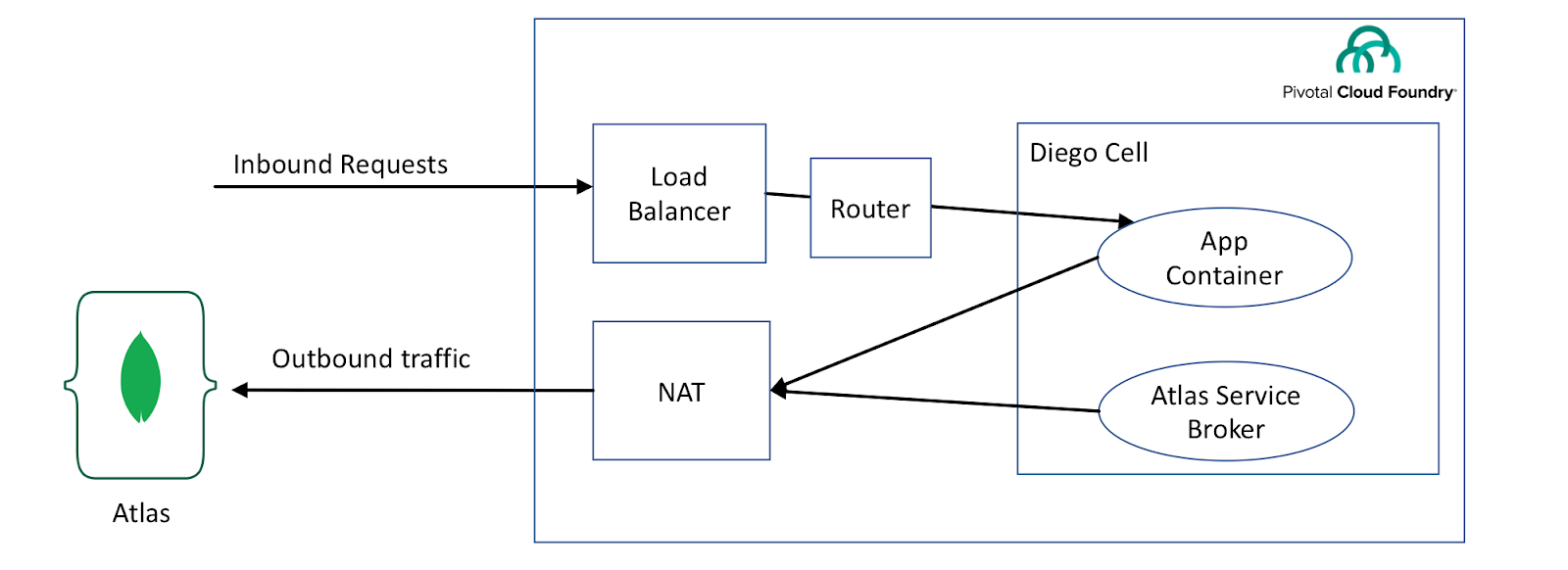
Without a NAT VM, you will require additional configurations, including configuring all Diego Cells with a static public IP which will then need to be added to Atlas IP Whitelist. This is not ideal and can get complicated very quickly, especially when your Network topology keeps changing.
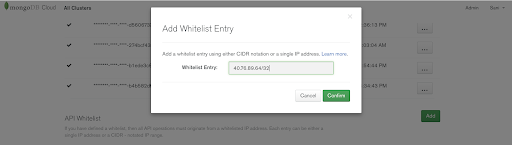
Now, let add the NAT VM public IP to Atlas API whitelist. If you testing this using PCF Dev, then this will simply be your laptop public IP. In the Atlas interface, and the account view, there is an API Whitelist section, on the upper right side of that section, click on the “Add” button.
Then add the NAT VM public IP as an entry
The last step is to define the Atlas tiers that you want to make available to the developers and deploy the Service Broker for Atlas. Here is the GitHub link to work through the process.
Let’s Check Out the Developer Experience
Let's check what plans are available in the marketplace by running the following command:
Command

$ cf marketplace -s mongodb-atlas-aws 

Text Output

$ cf marketplace -s mongodb-atlas-aws 
Getting service plan information for service mongodb-atlas-aws as admin...
OK

service plan description 
aws-dev Please use this for Dev (This is a multitenant environment) free
aws-qa Please use this for Qa paid
aws-prod Please use this for any Production deploiement paid
aws-global_cluster Please use this for any Production deployment that requires global cluster. It includes 2 zones in US_EAST and US_CENTRAL paid

Here we can see the list of plans we have previously configured.
Now let request a MongoDB cluster for our Dev environment by issuing the following command:
Command

$ cf create-service mongodb-atlas-aws aws-dev dev-db

Text Output

Creating service instance dev-db in org pcfdev-org / space pcfdev-space as admin...
OK

Create in progress. Use 'cf services' or 'cf service dev-db' to check operation status.

Since this is an asynchronous process, you can check the provisioning progress by running the following command:
Command

$ cf service dev-db

Text Output

Showing info of service dev-db in org pcfdev-org / space pcfdev-space as admin...

name: dev-db
service: mongodb-atlas-aws
tags: 
plan: aws-dev
description: MongoDB Atlas Service on AWS
documentation: 
dashboard: https://cloud.mongodb.com/v2/5bf305dbf2a30bc3a008384f#clusters

Showing status of last operation from service dev-db...

status: create succeeded
message: 
started: 2018-11-19T18:50:07Z
updated: 2018-11-19T18:52:14Z

There are no bound apps for this service.

What happened here is that a project has been created and its IP Whitelist configuration adjusted to allows connection from any application living inside PCF. Then the cluster was deployed inside that project according to the selected plan (i.e: tier). This process took about 1-2 minutes.
A dashboard URL is returned, which gives you access to the project within Atlas.
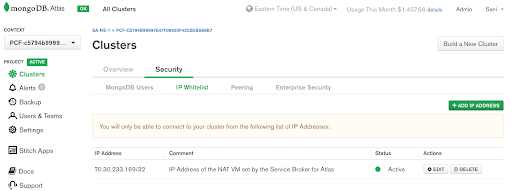
You can also verify that the project IP Whitelist has been properly configured to allow communication from the PCF environment.
Now as a developer, we might want to bind the newly created cluster to your existent application. This is achieved by “binding” your app to a service. You do that by running the following command:
Command

$ cf bind-service spring-music dev-db

Text Output

Binding service dev-db to app spring-music in org pcfdev-org / space pcfdev-space as admin...
OK
TIP: Use 'cf restage spring-music' to ensure your env variable changes take effect

In the command above I’m using the Spring Music app.
Once that command was issued, the service broker created a database user and granted it the Atlas admin role. A password was also randomly generated for that user and returned to the application, along with the connection string. The application can then just leverage that information to connect to the new cluster.
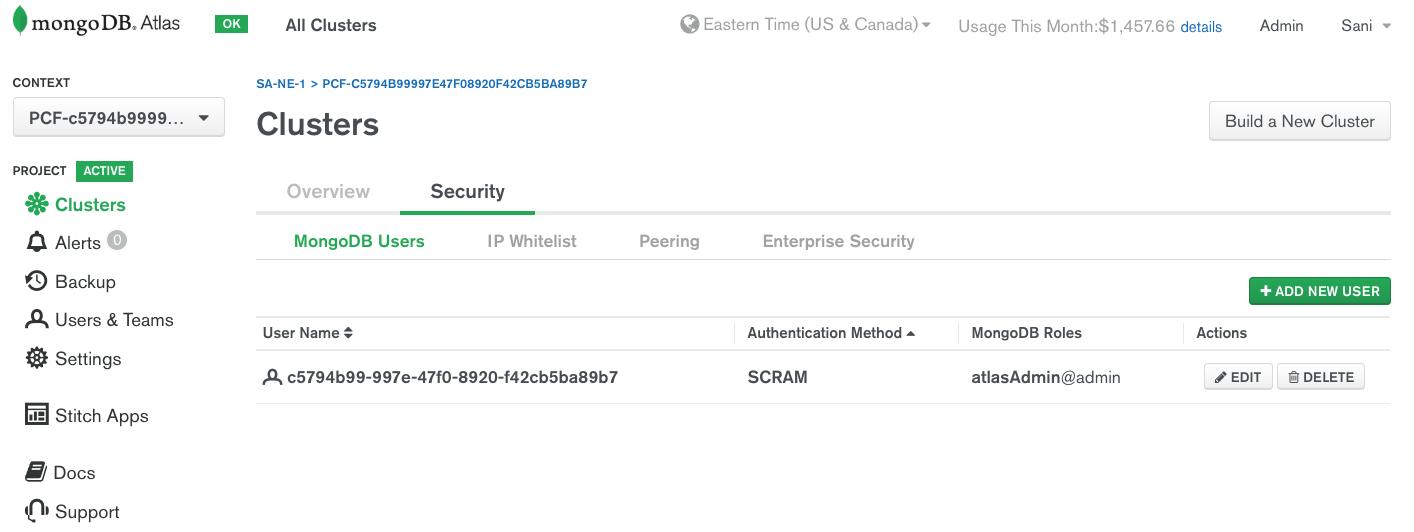
On the Atlas dashboard, you can check that a user has indeed been successfully created.
Finally, we can verify in PCF that they have been successfully added to the application environment variables by issuing the following command:
Command

$ cf env spring-music 

Text Output

Getting env variables for app spring-music in org pcfdev-org / space pcfdev-space as admin...
OK

System-Provided:
{
 "VCAP_SERVICES": {
 "mongodb-atlas-aws": [
 {
 "credentials": {
 "database": "test",
 "groupId": "5bf305dbf2a30bc3a008384f",
 "mongodbUri": "mongodb+srv://79f7e2411058421aa5692fae44f0f0de-4xa0q.mongodb.net/test?retryWrites=true",
 "password": "FH0m92BeSDJj",
 "uri": "mongodb+srv://79f7e2411058421aa5692fae44f0f0de-4xa0q.mongodb.net/test?retryWrites=true",
 "username": "79f7e241-1058-421a-a569-2fae44f0f0de"
 },
 "label": "mongodb-atlas-aws",
 "name": "dev-db",
 "plan": "aws-dev",
 "provider": null,
 "syslog_drain_url": null,
 "tags": [
 "MongoDB",
 "Atlas",
 "AWS"
 ],
 "volume_mounts": []
 }
 ]
 }
}

Conclusion
With a service broker for Atlas, the world is truly yours. If you are a platform engineer leveraging Cloud Foundry in your enterprise, then you already know that an important part of your job is about bringing value into the platform and reduce complexity/redundancies as much as possible. A Service Broker for Atlas can help better deliver on that promise.